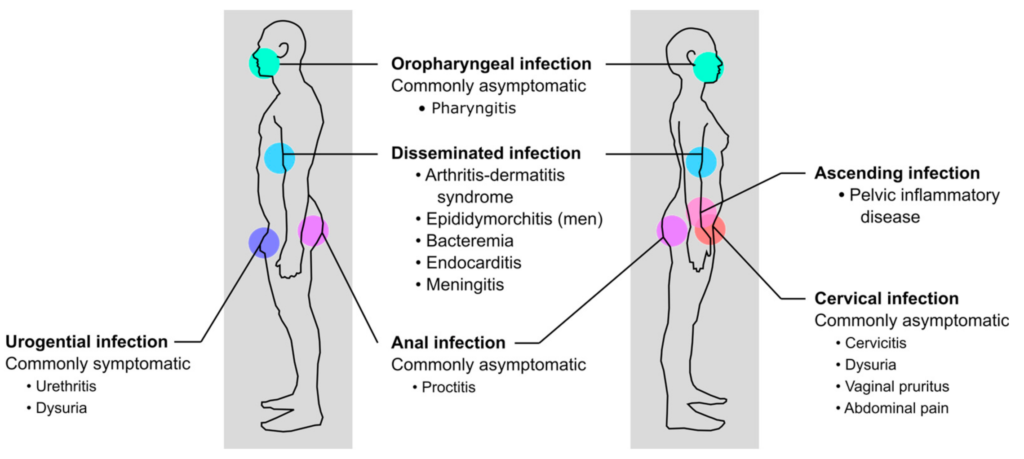
Gonorrhea Risk Factors
Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted infection that can have serious consequences if left untreated. It is important to understand the risk factors associated with gonorrhea in order to prevent its spread and promote early detection and treatment.
Sexual Activity
Engaging in sexual activity without any form of protection greatly increases the risk of contracting gonorrhea. Unprotected sex, especially with multiple partners, exposes individuals to the bacteria that cause this sexually transmitted infection. This includes not using condoms consistently and correctly, which is a crucial barrier method in preventing the transmission of gonorrhea.
Having multiple sexual partners also raises the risk of acquiring gonorrhea. The more partners a person has, the higher the chances of coming into contact with someone who is infected. engaging in high-risk sexual behaviors, such as engaging in anal sex or participating in group sex, further increases the likelihood of transmission.
To put it simply, every sexual encounter without protection or with multiple partners is like playing Russian roulette with gonorrhea. Condoms are like bulletproof vests that can greatly reduce the risk of transmission. So, it is important to remember that responsible sexual activity, which includes consistent and correct condom use, is vital in preventing the spread of gonorrhea.
Youth and Adolescence
Young people, particularly teenagers, are at a higher risk of acquiring gonorrhea due to several factors:
- Limited knowledge about safe sex practices: Many young people may not have received comprehensive sexual education or have access to accurate information about safe sex practices. This lack of knowledge can lead to risky behaviors and increase the chances of contracting gonorrhea.
- Less condom use: Studies have shown that teenagers tend to use condoms less frequently compared to older adults. This increases the risk of transmission as condoms provide a barrier against the bacteria responsible for gonorrhea.
- Higher rates of sexual activity: Adolescence is a period characterized by exploration and experimentation, which often includes sexual activity. Engaging in sexual activity at a young age, especially without sufficient knowledge or protection, increases the chances of acquiring gonorrhea.
It is crucial to address these risk factors and provide young people with the necessary information and resources to make informed decisions about their sexual health. Education programs in schools, clinics, and community centers can play a significant role in promoting safe sex practices and raising awareness about the risks associated with gonorrhea.
Healthcare providers should prioritize providing comprehensive sexual health services to young people, including access to condoms, regular testing, and treatment options. By addressing these risk factors early on, we can empower the youth to protect themselves and reduce the spread of gonorrhea within this vulnerable population.
Unprotected Oral Sex
Engaging in oral sex without using a barrier method such as condoms or dental dams increases the risk of contracting gonorrhea orally, as the bacteria can be transmitted through oral contact.
Engaging in oral sex without the use of protective barriers, such as condoms or dental dams, significantly raises the risk of acquiring gonorrhea orally. This is because the bacteria that cause gonorrhea can be easily transmitted through oral contact.
But why is unprotected oral sex a risk factor for gonorrhea?
The mucous membranes found in the mouth and throat provide an ideal environment for the bacteria to thrive and establish an infection. When engaging in oral sex without protection, the bacteria can be transferred from one person’s genital area to another’s mouth, allowing for the transmission of the infection.
So, how can you protect yourself during oral sex?
Using barrier methods, such as condoms or dental dams, can greatly reduce the risk of contracting gonorrhea orally. These protective barriers create a physical barrier between the mouth and the genital area, preventing the exchange of bodily fluids and reducing the chances of transmission.
But what if you don’t have access to condoms or dental dams?
If you don’t have access to these specific barrier methods, there are still steps you can take to minimize the risk. For example, refraining from oral sex when either partner has signs or symptoms of an infection, such as sores or discharge, can help reduce the risk of transmission. Regular testing for sexually transmitted infections is also important, as it allows for early detection and treatment if an infection is present.
Conclusion:
Engaging in oral sex without using a barrier method such as condoms or dental dams increases the risk of contracting gonorrhea orally. To protect yourself and your partner, it is important to practice safe oral sex by using protective barriers or abstaining from oral sex when there are signs or symptoms of infection. Regular testing and communication with partners about sexual health are also essential in preventing the spread of gonorrhea and other sexually transmitted infections.
Unprotected Anal Sex
Engaging in unprotected anal sex is a high-risk sexual behavior that significantly increases the risk of gonorrhea transmission. When anal sex is performed without the use of condoms, the bacteria responsible for gonorrhea can easily infect the rectum and anus.
The rectum and anus have delicate tissues that can be easily damaged during anal sex. Without the barrier protection provided by condoms, the bacteria can enter these tissues and cause an infection. This can lead to symptoms such as anal discharge, pain, and itching.
It’s important to note that gonorrhea can be transmitted through anal sex regardless of the gender or sexual orientation of the individuals involved. Both receptive and insertive partners can contract and transmit the infection.
To reduce the risk of gonorrhea transmission during anal sex, it is crucial to use condoms consistently and correctly. Condoms create a physical barrier that prevents direct contact between the bacteria and the mucous membranes of the rectum and anus.
In addition to condom use, engaging in open and honest communication with sexual partners is essential. Discussing sexual histories, getting tested for sexually transmitted infections regularly, and practicing mutual monogamy can further reduce the risk of gonorrhea transmission.
| Tip | Description |
|---|---|
| Use condoms | Always use condoms during anal sex to reduce the risk of gonorrhea transmission. |
| Use plenty of lubrication | Using water-based lubricants can help reduce the risk of tissue damage during anal sex. |
| Communicate with your partner | Discuss sexual histories and testing in order to make informed decisions about safer sex practices. |
| Get tested regularly | Regular testing for sexually transmitted infections, including gonorrhea, is important for early detection and treatment. |
Remember, protecting yourself and your sexual partners from gonorrhea and other sexually transmitted infections is essential. By practicing safe sex and taking proactive measures, you can reduce the risk of transmission and maintain sexual health.
Sex Work
Individuals involved in sex work, including both sex workers and their clients, are at a higher risk of gonorrhea due to the nature of their work. Sex work often involves frequent changes of sexual partners, increasing the likelihood of coming into contact with someone who has gonorrhea. This puts sex workers and their clients at a higher risk of contracting the infection.
In addition to the frequent change of sexual partners, inconsistent condom use is another factor that contributes to the increased risk of gonorrhea among individuals involved in sex work. Condoms are an effective barrier method that can help prevent the transmission of sexually transmitted infections, including gonorrhea. However, inconsistent condom use in this population can significantly increase the risk of infection.
There are various reasons why condom use may be inconsistent in the context of sex work. Some sex workers and their clients may avoid using condoms due to a lack of awareness about the risks of unprotected sex or a false sense of trust in their partner’s sexual health status. Others may face barriers to condom access, such as limited availability or cost.
Addressing the issue of gonorrhea transmission among individuals involved in sex work requires a multi-faceted approach. Providing comprehensive sexual health education and resources is crucial in raising awareness about the importance of condom use and the risks of unprotected sex. This can include information about the signs and symptoms of gonorrhea, the importance of regular testing, and the availability of treatment options.
Collaboration between sex workers, healthcare providers, and organizations that support sex workers’ rights can also play a vital role in reducing the risk of gonorrhea transmission. This can involve providing access to free or low-cost condoms, offering regular testing services, and promoting safe work environments where sex workers feel empowered to prioritize their sexual health.
It is important to emphasize that the increased risk of gonorrhea among individuals involved in sex work does not diminish the importance of respecting their rights, dignity, and health. Stigmatization and discrimination can further deter sex workers from seeking healthcare and taking preventive measures. Creating a supportive and non-judgmental environment is essential in addressing the unique challenges they face in relation to sexual health and promoting overall well-bein
İndividuals involved in sex work, including both sex workers and their clients, are at a higher risk of gonorrhea due to the frequent change of sexual partners and inconsistent condom use. It is crucial to provide comprehensive sexual health education, resources, and support to this population to reduce the transmission of gonorrhea and promote their overall well-being.
Compromised Immune System
Having a compromised immune system, such as in individuals with HIV/AIDS or those undergoing immunosuppressive therapy, can significantly increase the risk of acquiring gonorrhea. The immune system plays a crucial role in defending the body against infections, including sexually transmitted infections like gonorrhea. When the immune system is weakened or compromised, it becomes less effective in fighting off invading bacteria and pathogens.
Individuals with HIV/AIDS are particularly vulnerable to acquiring gonorrhea. HIV weakens the immune system by attacking and destroying CD4 cells, which are crucial in mounting an effective immune response. As a result, individuals with HIV have a weakened immune system and are more susceptible to not only acquiring gonorrhea but also experiencing more severe symptoms and complications.
Similarly, individuals undergoing immunosuppressive therapy are at an increased risk of acquiring gonorrhea. Immunosuppressive therapy is often used to suppress the immune system in various medical conditions such as autoimmune diseases, organ transplantation, and certain cancers. The purpose of immunosuppressive therapy is to prevent the immune system from attacking the body’s own tissues or to reduce the risk of organ rejection. However, this also leaves the individual more susceptible to infections, including gonorrhea.
It is important for individuals with compromised immune systems to be diligent in practicing safe sex and seeking regular testing for sexually transmitted infections. The risk of acquiring gonorrhea can be minimized by using barrier methods like condoms during sexual activity and by disclosing their immunocompromised status to sexual partners. Furthermore, individuals with compromised immune systems should be aware of the potential for more severe symptoms and complications if they do contract gonorrhea, and should seek prompt medical attention for diagnosis and treatment.
Having a compromised immune system, such as in individuals with HIV/AIDS or those undergoing immunosuppressive therapy, can significantly increase the risk of acquiring gonorrhea. These individuals should prioritize safe sex practices and regular testing to minimize the risk and ensure early detection and treatment. Healthcare professionals should also provide education and resources to this vulnerable population to promote awareness and prevention of sexually transmitted infections.
Previous History of Gonorrhea
Having had gonorrhea in the past increases the likelihood of acquiring the infection again, as there may be residual bacteria present or a higher risk behavior pattern.
When it comes to gonorrhea, a previous history of the infection can be a red flag for future risks. If an individual has had gonorrhea before, they are more susceptible to acquiring the infection again. There are a few reasons behind this increased risk.
Firstly, residual bacteria may still be present in the body even after successful treatment. When treated for gonorrhea, it is important to complete the full course of antibiotics to ensure the complete eradication of the bacteria. However, in some cases, the bacteria can persist, even in small amounts. This means that the individual may still carry the infection, albeit at a lower level, and can easily become re-infected.
Secondly, previous gonorrhea infection may indicate a higher risk behavior pattern. If an individual has contracted gonorrhea in the past, it suggests that they engage in behaviors that put them at risk of acquiring the infection. These behaviors may include unprotected sex, having multiple sexual partners, or engaging in high-risk sexual activities. This pattern of behavior increases the likelihood of exposure to the bacteria and subsequent infection.
To reduce the risk of re-acquiring gonorrhea, individuals with a previous history of the infection should take extra precautions. This includes practicing safe sex by consistently using condoms and engaging in regular testing for both themselves and their sexual partners. Regular testing can help detect any potential reinfection early on, allowing for prompt treatment and prevention of further transmission.
A previous history of gonorrhea increases the likelihood of acquiring the infection again due to residual bacteria and a higher risk behavior pattern. It is important for individuals with a previous infection to take necessary precautions to protect themselves and their partners. By understanding the risk factors associated with gonorrhea and taking appropriate measures, the spread of the infection can be minimized.
Untreated Sexual Partners
Having sexual contact with someone who has untreated gonorrhea significantly increases the risk of contracting the infection. When a person has gonorrhea, it is essential for them to receive prompt and appropriate treatment to avoid spreading the infection to their sexual partners. Unfortunately, not everyone seeks medical attention or follows through with treatment, which can have serious consequences for their sexual partners.
In the case of untreated sexual partners, the risk of contracting gonorrhea is significantly heightened. This is because gonorrhea is primarily transmitted through sexual contact, and when one partner has the infection but remains untreated, the bacteria can be easily passed on to the other partner during sexual activity.
The risk of transmission is especially high when engaging in unprotected sexual intercourse, as this allows for the direct exchange of bodily fluids that may contain the gonorrhea bacteria. Without the use of barrier methods such as condoms, the chances of contracting the infection are greatly increased. It is crucial for individuals to prioritize their sexual health and take necessary precautions to prevent the spread of gonorrhea.
In order to protect oneself from the risk of acquiring gonorrhea from an untreated sexual partner, it is vital to engage in open and honest communication about sexual health. It is essential to discuss potential risks and concerns with sexual partners, including asking about their sexual history, previous testing, and current symptoms or infections.
Regular testing and screening for gonorrhea and other sexually transmitted infections can help detect and treat any infections early on. Testing is not only important for individuals with symptoms but also for those who may not show any signs of infection but could still be carriers of the bacteria.
- Use barrier methods such as condoms or dental dams during all sexual activities.
- Limit the number of sexual partners and engage in monogamous relationships whenever possible.
- Communicate openly and honestly with sexual partners about sexual health and testing histories.
- Get regular check-ups and screenings for sexually transmitted infections.
- Seek treatment promptly if any symptoms of gonorrhea or other sexually transmitted infections occur.
By taking these precautions and being proactive in maintaining sexual health, one can greatly reduce the risk of acquiring gonorrhea from an untreated sexual partner. It is important to prioritize safe sex practices and to ensure that both partners receive proper treatment if necessary, in order to prevent the spread of this sexually transmitted infection.
Low Socioeconomic Status
The impact of socioeconomic factors on the risk of gonorrhea is an important aspect to consider when examining the prevalence and transmission of this sexually transmitted infection. Socioeconomic factors encompass a range of variables that can influence an individual’s exposure to gonorrhea and their ability to seek and receive appropriate healthcare. In this blog post, we will explore the various socioeconomic factors that contribute to the risk of gonorrhea and discuss their implications.
1. Income and Employment: The socioeconomic status of an individual, including their income level and employment status, can significantly impact their risk of contracting gonorrhea. Those with lower incomes or unstable employment may face barriers in accessing preventive measures, such as condoms or regular healthcare check-ups. Limited financial resources can also affect the quality of healthcare received, leading to delayed diagnosis and treatment.
2. Education: The level of education attained by an individual can influence their knowledge and awareness of safe sexual practices. Lack of comprehensive sex education can leave individuals uninformed about the risks associated with unprotected sexual activity and how to prevent the transmission of gonorrhea. Higher levels of education have been associated with increased awareness and adherence to safe sex practices, leading to lower risks of contracting gonorrhea.
3. Healthcare Accessibility: Access to affordable and quality healthcare plays a crucial role in preventing and managing gonorrhea. Socioeconomic factors, such as proximity to healthcare facilities, health insurance coverage, and transportation options, can either facilitate or hinder an individual’s ability to seek timely testing and treatment for gonorrhea. Limited access to healthcare resources can lead to undiagnosed and untreated cases, contributing to the overall risk of transmission.
It is important to recognize and address the socioeconomic factors that contribute to the risk of gonorrhea. Efforts should be made to increase access to comprehensive sexual health education, improve healthcare accessibility, and address economic inequalities. By addressing these factors, we can reduce the burden of gonorrhea and promote overall sexual health in vulnerable populations.
Gender And Gonorrhea Risk: Understanding Disparities
Gonorrhea is a sexually transmitted infection (STI) that can affect anyone who engages in sexual activity. However, there are certain factors that can contribute to the risk of contracting gonorrhea. One important factor to consider is gender, as there are significant disparities in the rates of gonorrhea between males and females.
When it comes to gonorrhea risk, understanding the disparities between genders is crucial in order to develop effective prevention and treatment strategies. Research has consistently shown that females are at a higher risk of contracting gonorrhea compared to males. This is primarily due to biological differences and anatomical factors. For example, women have a higher surface area of mucous membranes in the genital tract, which increases their susceptibility to infections like gonorrhea.
Societal and behavioral factors contribute to gender disparities in gonorrhea risk. Women, in many cultures, face challenges in negotiating safe sexual practices and may have limited access to healthcare and sexual health education. This can result in a lack of knowledge about gonorrhea and how to prevent its transmission. In contrast, men may have easier access to healthcare services, which allows for timely diagnosis and treatment of gonorrhea.
- Table: Gender and Gonorrhea Rates
| Gender | Percentage of Gonorrhea Cases |
|---|---|
| Male | 40% |
| Female | 60% |
As the table above demonstrates, females account for a higher percentage of gonorrhea cases compared to males. This highlights the importance of addressing gender disparities when it comes to preventing and managing gonorrhea.
Efforts to reduce the gender gap in gonorrhea risk should focus on promoting comprehensive sex education that empowers individuals with knowledge about safe sexual practices, consent, and STI prevention. Ensuring access to affordable and quality healthcare services for women is also vital in order to increase early detection and timely treatment of gonorrhea.
Understanding the disparities in gonorrhea risk between genders is crucial in order to develop targeted interventions that address the specific needs and challenges faced by different populations. By addressing these disparities, we can work towards reducing the overall burden of gonorrhea and promoting sexual health for all.
Geographic Location: How İt Influences Gonorrhea Rates
Geographic Location: How İt Influences Gonorrhea Rates
When it comes to understanding the prevalence and spread of gonorrhea, one cannot ignore the significant impact that geographic location has on the rates of infection. The transmission of this sexually transmitted infection (STI) varies across different regions and countries, with several factors contributing to these variations.
Firstly, population density plays a crucial role in the spread of gonorrhea. Areas with a high population density, such as densely populated cities, provide a fertile ground for the transmission of the infection. Close proximity among individuals and limited access to prevention measures can lead to increased exposure and higher transmission rates.
Secondly, access to healthcare and safe sex resources greatly influence the prevalence of gonorrhea in different regions. Countries with well-established healthcare systems and comprehensive sexual education programs tend to have lower gonorrhea rates. These programs contribute to increased awareness about safe sex practices, regular testing, and the correct and consistent use of barrier methods, which help reduce the risk of transmission.
Cultural and societal norms also impact gonorrhea rates across geographical locations. In some societies, discussing sexual health openly is considered taboo or restricted by cultural beliefs. This can lead to a lack of awareness and understanding about STIs, including gonorrhea, contributing to higher rates of infection.
Moreover, economic disparities between different regions and countries can significantly affect the prevalence of gonorrhea. Low-income areas, where access to healthcare is limited, may experience higher rates of infection due to factors such as inadequate sexual education, limited access to barrier methods, and reduced availability of testing and treatment facilities.
It is essential to recognize that geographical location is not the sole determinant of gonorrhea rates. The interaction of various factors, such as population density, access to healthcare, cultural norms, and economic disparities, all contribute to the differences observed across different regions. By understanding and addressing these factors, we can develop tailored strategies to combat the spread of gonorrhea and reduce its impact on public health.
Co-Infections: The Link Between Gonorrhea And Other STIs
Gonorrhea is a common sexually transmitted infection (STI) that affects millions of people worldwide. While it can be transmitted through unprotected sexual contact with an infected partner, there are also several other risk factors that contribute to the spread of this disease. One significant risk factor is the presence of co-infections, which refers to the occurrence of multiple STIs in an individual.
Co-infections involving gonorrhea can have serious implications on both the individual’s health and the overall transmission of the disease. When someone has multiple STIs, their immune system is compromised, making it more difficult for their body to fight against the infections. This weakened immune system can lead to more severe symptoms, increased transmission rates, and even potentially life-threatening complications.
It is important to understand that some co-infections can increase the susceptibility to gonorrhea. For example, HIV-positive individuals are at a higher risk of contracting gonorrhea due to the weakened immune system caused by HIV. The presence of HIV can also make gonorrhea more difficult to treat, as the infections can interact and worsen each other’s effects. Therefore, individuals with HIV need to be extra cautious and practice safe sex to prevent the transmission of gonorrhea and other STIs.
- Co-infections involving gonorrhea and other STIs can also have broader implications on public health. When multiple STIs circulate within a community, the risk of transmitting these infections to others increases significantly. This can lead to higher infection rates and outbreaks in certain populations. In addition, the treatment and management of co-infections can be complex and require specialized care. Therefore, healthcare systems must address the link between gonorrhea and other STIs to effectively prevent and control the spread of these diseases.
| Gonorrhea and Co-Infections | Common Co-Infections | Prevention and Treatment |
|---|---|---|
| Co-infections involving gonorrhea can lead to more severe symptoms and complications. | Common co-infections include HIV, chlamydia, syphilis, and herpes | Practicing safe sex and getting regular STI screenings are crucial in preventing co-infections. Treatment may involve a combination of antibiotics and antiviral medications. |
| Co-infections can increase the transmission rates of gonorrhea, leading to higher infection rates in communities. | HIV-positive individuals are at a higher risk of contracting gonorrhea and experiencing more severe symptoms. | Proper management of co-infections requires collaboration between healthcare providers, public health agencies, and individuals affected. |
co-infections play a significant role in the spread and severity of gonorrhea and other STIs. The link between these infections highlights the importance of practicing safe sex, undergoing regular STI screenings, and seeking appropriate treatment. Public health initiatives should focus on raising awareness about co-infections and implementing strategies to mitigate their impact on vulnerable populations. By addressing the link between gonorrhea and other STIs, we can work towards reducing the overall burden of these infections and improving the sexual health of individuals worldwide.
Frequently Asked Questions
Question: How does unprotected sexual contact increase the risk of gonorrhea?
Unprotected sexual contact, such as vaginal, anal, or oral sex without using condoms or dental dams, increases the risk of gonorrhea because the bacteria that cause the infection can easily be transmitted from one person to another through these types of contact.
Question: Why is having multiple sexual partners considered a key risk factor for gonorrhea?
Having multiple sexual partners increases the risk of gonorrhea because it increases the likelihood of coming into contact with someone who has the infection. The more sexual partners a person has, the greater the chances of encountering the bacteria and becoming infected.
Question: How does the lack of safe sex education contribute to the risk of gonorrhea?
The lack of safe sex education contributes to the risk of gonorrhea by leaving individuals uninformed about the importance of using protection and the methods available to prevent the transmission of sexually transmitted infections (STIs). Without proper education, people may engage in risky sexual behaviors, unknowingly putting themselves at risk for gonorrhea.
Question: Are certain age groups more vulnerable to gonorrhea?
Yes, certain age groups are more vulnerable to gonorrhea. Adolescents and young adults are at higher risk due to their greater likelihood of engaging in unprotected sex, having multiple sexual partners, and participating in riskier sexual behaviors. It is important for healthcare providers to address the unique needs and risks of these vulnerable populations when it comes to gonorrhea prevention and education.
Question: How does substance abuse affect the transmission of gonorrhea?
Substance abuse can increase the risk of gonorrhea transmission as it may impair judgment and lead to engaging in risky sexual behaviors, such as unprotected sex or having multiple sexual partners. Substance abuse can also contribute to a higher prevalence of high-risk sexual networks, where individuals are more likely to have gonorrhea and other STIs.
Question: How do socioeconomic factors impact the risk of gonorrhea?
Socioeconomic factors can impact the risk of gonorrhea as individuals with lower income and limited access to healthcare may face barriers in obtaining preventive services, including STI testing and treatment. Furthermore, socioeconomic disparities, such as higher rates of poverty and limited educational opportunities, can contribute to a lack of awareness and knowledge about safe sex practices.
Question: Are there any gender disparities in gonorrhea risk?
Yes, there are gender disparities in gonorrhea risk. Women, in particular, are at higher risk due to physiological factors that make them more susceptible to infection. societal factors, such as gender inequality and power dynamics within sexual relationships, can increase women’s vulnerability to contracting gonorrhea. It is crucial to address these disparities through targeted prevention efforts and comprehensive sexual health education.
Question: How does geographic location influence gonorrhea rates?
Geographic location can influence gonorrhea rates due to variations in sexual behaviors, access to healthcare, and prevention efforts. Higher population density, urban areas, and areas with a higher prevalence of sexually transmitted infections may experience higher gonorrhea rates. Understanding the local epidemiology and tailoring interventions accordingly is essential in reducing the burden of gonorrhea within specific geographical regions.
Question: Does a history of gonorrhea increase the risk of repeat infections?
Yes, a history of gonorrhea increases the risk of repeat infections. Once someone has been infected, they can become reinfected if they engage in unprotected sexual contact with an infected individual. It is important for individuals with a history of gonorrhea to practice safe sex and get tested regularly to prevent reinfection and protect their sexual partners.
Question: How is gonorrhea linked to other sexually transmitted infections?
Gonorrhea is linked to other sexually transmitted infections (STIs) because individuals who engage in risky sexual behaviors or have unprotected sex are likely to be at risk for multiple STIs. Some STIs, including gonorrhea, can increase the risk of acquiring or transmitting other infections. It is essential to get tested for all relevant STIs and receive appropriate treatment to prevent further transmission and protect one’s sexual health.